Table of Contents
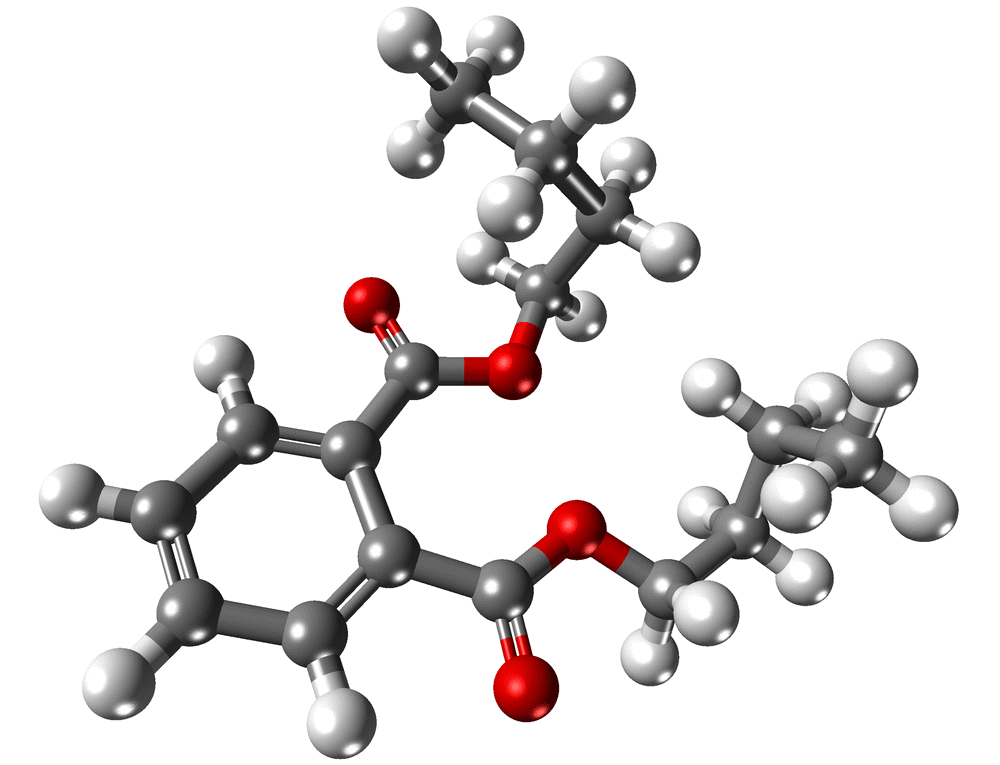
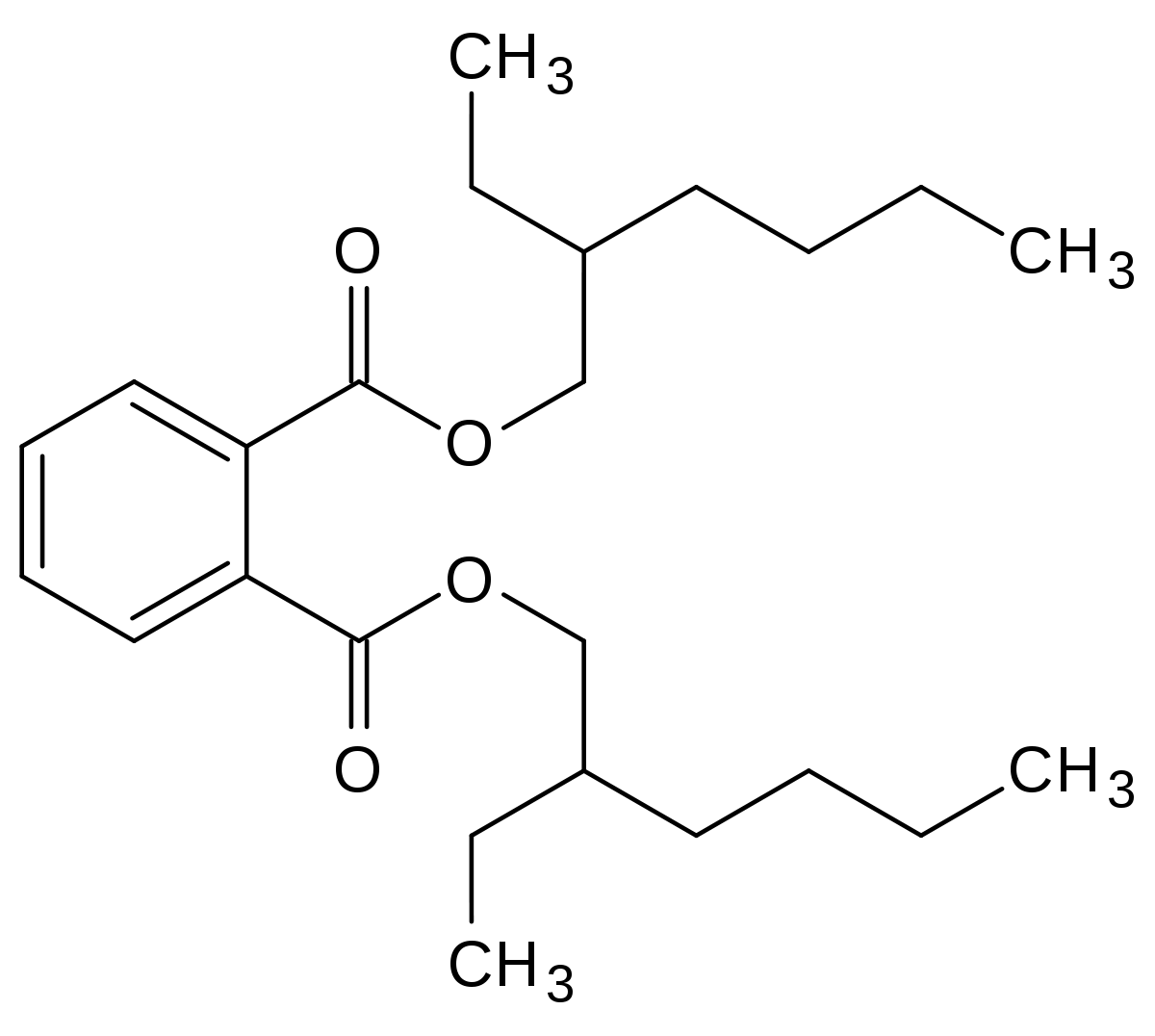
Dioctyl phthalate (DOP), also known as diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4 (CO2C8H17). Dioctyl phthalate, characterized by its molecular weight, high boiling point, and low vapor pressure, is one of the most widely used general emollients. It is synthesized by the reaction of phthalic anhydride with an chemical alcohol such as 2-ethyl hexanol. Dioctyl phthalate or DOP is a softener used in the production of flexible polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastics. Dioctyl phthalate or DOP is insoluble in water and has good stability against heat, ultraviolet light, wide compatibility, and has excellent resistance to hydrolysis.
Molecular structure of DOP
Uses and applications of dioctyl phthalate (DOP) in daily life
Dioctyl phthalate (DOP) is used in PVCs, polyvinyl acetate, rubbers, cellulose plastics, and polyurethanes. The final uses of DOP are:

Application of Dioctyl phthalate in films
- Producing Flooring and wallpaper
- Manufacturing Artificial leather
- Producing PVC foams
- Manufacturing Films
- Producing Viscous materials such as polyurethane or polysulfide adhesives and colored adhesives

Application of DOP in adhesives
Dioctyl phthalate or DOP, is one of the most widely used emollients in a variety of applications such as cables, wires, films, papers, medical device resins, walls, and floors.
DOP or Dioctyl phthalate manufacturing process
All manufacturers of phthalate esters use the same processes. Dioctyl phthalate (DOP) is manufactured by phthalic sterilization of anhydride with 2-ethyl-hexanol. This reaction occurs in two successive stages. The first stage of the reaction leads to the formation of a monoester by the de-alcoholization of phthalic acid, this step is completed quickly.
The second step of the production of dioctyl phthalate involves converting the monoster to a diester. This is a reversible reaction and proceeds more slowly than the first reaction. To change the equilibrium towards the diester, the reaction water is removed by distillation. High temperatures and catalysts accelerate the reaction rate. Depending on the catalyst used, the temperature in the second stage varies from 140 ° C to 165 ° C with acidic catalysts and from 200 ° C to 250 ° C with amphoteric catalysts.
Purity changes may occur depending on the catalyst, the reacting alcohol, and the type of process. Excess alcohol is recovered and the Iran dioctyl phthalate (DOP) is purified by vacuum distillation. The reaction sequence is performed in a closed system. This process can be performed sequentially or in batches.
Dioctyle phthalate manufacturing process
Familiarity with different types of phthalates
Phthalates are a family of chemical compounds that are widely used as additives in a wide range of plastics and many consumer products, and primarily to make polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or flexible vinyl. Phthalates are one of the most common emollients in the world, which are classified into “large molecule” or “small molecule” phthalates, depending on the molecular weight.
Large molecule phthalates have 13-17 carbon atoms in their chemical structure, which makes them more durable. There is a wide range of phthalates, each with specific properties, applications, and health effects. In the European Union, the five most widely used phthalates have been investigated by the European Chemicals Agency: Dioctyl phthalate (DOP) or (DEHP), DBP, DINP, DIDP, BBP.
Dibutyl phthalate (DEHP)
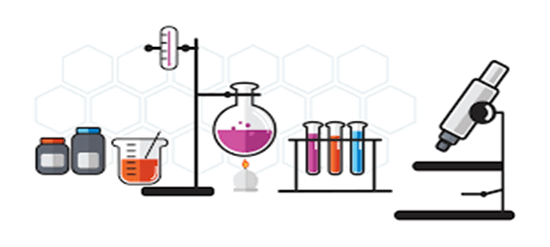
Dibutyl phthalate 3d structure
Di (2-Ethylhexyl) phthalate or DEHP No. [117-81-7] is also known as dioctyl phthalate (DOP). The production process of dioctyl phthalate is simple; Dioctyl phthalate (DOP) is the phthalate ester of 2-ethyl hexanol alcohol, which is normally produced by the dimerization of butyraldehyde, butyraldehyde is synthesized from propylene.
Di (2-Ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) is a plastic softener that offers good all-round performance and is therefore cost-effective for many products, including building materials such as floors, cables, profiles, and roof membranes, as well as products. It is used in medicine such as blood bags and dialysis equipment.
Di (2-Ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) has reasonable plasticity, fusion rate, and reasonable viscosity (for plastisol applications). The amount of DEHP in flexible polymeric materials varies but is often around 30% (by weight).
Molecular structure of DEHP
What is Dioctyl terephthalate or DOTP?
With the advancement of technology, dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP) entered the market as a supplement and enhancer of dioctyl phthalate (DOP). Iran Dioctyl phthalate One of the most effective methods for disposing of polyethylene terephthalate waste is the production of dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP) by alcohol.
Dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP) obtained from alcohol is used as a softener, especially for the production of polyvinyl chloride, and is one of the most widely used softeners due to its low cost.
Its emollients are additives, which by adding them to a special substance, increase the flexibility and softness of the material and make it easier to process and work with the material. These softeners, when added to materials, occupy the intermolecular space and increase the distance between the molecules. This phenomenon leads to greater flexibility and elasticity of materials.
Dioctyl terephthalate 3D structure
According to research, the direct addition of polyethylene terephthalate to the concrete mix for construction materials was eliminated and instead of using it directly in construction materials, the alcoholic product obtained from polyethylene terephthalate was used in the concrete slurry.
The effect of dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP) on concrete slurry properties such as electrical, mechanical, and fluidity properties were analyzed using the response surface methodology and compared with polyethylene terephthalate concrete admixture.
The results showed that the electrical strength of concrete increased with an increasing amount of dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP). The optimal slurry of dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP) has 29.90 times higher electrical resistance than the reference concrete slurry.
In addition, 10% of dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP) concrete with thermal conductivity of less than 30.3% has an electrical resistance of more than 657.7%. To produce corrosion-resistant concrete mortar, dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP) should be used instead of polyethylene terephthalate.
This branching structure has many superior properties compared to other emollients in dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP). Some of these properties include low volatility (resulting in stable properties to composite structures), low viscosity (greater fluidity), non-carcinogenicity (absence of ortho-phthalates), and high electrical resistance.
Currently, Dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP) is one of the most widely used plastic softeners in the United States, Europe, and Russia due to its unique properties. Building materials have always been a useful option for disposing of solid waste because these wastes, such as WPET, provide thermal properties, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance in the building.
However, when the use of WPET solid waste exceeds certain values, they cause problems such as decomposition, separation of the cement structure, or shrinkage on one side of the concrete.
Dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP) is a more homogeneous mixture when used with cement paste than WPET, and DOTP (DOCEM) cement mortar is about 7.6 times more electrically resistant than WPET (WPETCEM) cement mortar.
Uses and benefits of Iran phthalates
Large molecule phthalates, such as dioctyl phthalate (DOP), are colorless, odorless, and are used in many products that require high performance, longevity, and durability. Due to their high performance, durability, and stability, large molecule phthalates are primarily used to soften or “plasticize” vinyl. They adhere tightly to the vinyl structure and do not evaporate easily.
Although they can be used in a variety of applications, different types of large molecule phthalates are not necessarily modifiable. The unique properties of a phthalate such as dioctyl phthalate (DOP) usually make it suitable for a particular product and allow manufacturers to use (function and safety specifications) the appearance (texture, color, size, and shape). Durability and stability of phthalates to meet their unique needs.
Building materials and construction:
From suspended ceilings to flexible adhesives and sealants, durable interior cladding, dioctyl phthalate (DOP) is used to create a wide range of more durable vinyl surfaces and easier maintenance in construction applications. Buildings include vinyl siding, flexible flooring, wallpaper, soundproofing, waterproofing, and electrical insulation.

Application of phthalates as flooring
Wires and cables:
Large molecule phthalates are used in PVC insulation for electrical wiring that connects and supports electronic devices. For example, PVC may use dioctyl phthalate (DOP), which wires televisions and computers.
Some of the advantages of large molecule phthalates include low-temperature performance, flexibility, heat resistance, and electrical resistance.

Application of phthalates in cabling
Car and airline:
In-car interiors, such as seat covers and car interior decorations, use dioctyl phthalate (DOP) softened vinyl because of its durability, UV resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures. PVC coatings and components under the body in the car, help prevent corrosion, weather and can also be used as rocket propellants.
External products:
Because dioctyl phthalate (DOP) contributes to the flexible performance of PVC, it performs well in changing climatic conditions – maintaining flexibility in cold conditions and resisting high-temperature degradation – in many products. Outdoors such as swimming pools, garden hoses, and roof surfaces, and waterproof shoes are used.
Textiles:
Dioctyl phthalate, or DOP, is used in coated textiles to produce weather-resistant fabrics and luggage, as well as as a lubricant in textiles.

DOP in Textiles
Small molecule phthalates are also used primarily as solvents in perfumes to have a longer shelf life and are used in nail polish to prevent flaking. They are also used as insect repellents, as solvents in varnishes and pesticides, and as colorants.
Safety tips about Iran dioctyl phthalate manufacturing
Phthalates typically use emollients, so the global dioctyl phthalate (DOP) market is expected to see steady revenue growth in the new era. The main factors that are likely to drive the growth of the phthalic acid market are the increasing demand from industries such as film and paper, consumer goods, cables, and wiring, which has stimulated the global market for dioctyl phthalate (DOP) in the new era.
In addition, increased demand from developing regions of the world, especially from Asia-Pacific, is expected to grow further.
Also, the cost-effectiveness of dioctyl phthalate or DOP is another factor that prioritizes its use as an emollient. However, its use in some applications, such as those that have a direct and extensive relationship with food and medical devices, is being replaced by non-phthalate softeners, which is expected to hinder the growth of the global market. DOP phthalates in the new age.
The question here is, are phthalates safe? In recent years, many claims have been made about the effects of phthalates on health. Extensive scientific information on large phthalates provides consumers with information on the safety of phthalates and helps to dispel public confusion about large phthalates. Keep in mind.
Government agencies and regulators around the world have advocated the safety of large phthalates in commercial products. In addition, universities, government agencies, manufacturers, and laboratories have independently conducted extensive research on large molecule phthalates. It shows that large phthalates are broken down into metabolites within minutes of entering the body.
Data collected by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention over the past 10 years also show that exposure to all sources of phthalate together is very low, well below the level set by scientists in regulatory agencies.
In 2013, the European Chemicals Representative (ECHA) released a public assessment of the potential risks associated with the day-to-day use of DINP, dioctyl phthalate DOP, and DIDP.
They concluded that the healthy use of DINP, DOP, and DIDP for children and adults, including the use of gloves, shoes, children’s school supplies such as pencils, school bags, and erasers, shower curtains, artificial leather in homes and car interiors, coverings Walls and floors, wires and cables, etc. do not pose a health threat.
Our technical service staff has extensive professional experience in the field of manufacturing and sale of dioctyl phthalate (DOP) for domestic consumption and export of dioctyl phthalate (DOP) as well as gaining expertise in the fields of monitoring, assistance in setting up and optimizing performance. Are catalysts.
If you need more information on how to buy Dioctyl Phthalate (DOP) or the price of Dioctyl Phthalate (DOP), contact the company’s experts via the link below.
Moheb Baspar Petrochemical Company Idea Gostar

