By adding 5 to 10% polybutadiene during the polymerization process and creating chemical bonds and forming a double bond of butadiene with some free radicals of polystyrene, a copolymer and a two-phase mixture containing dispersed particles of one phase in another are produced. The final product at the end of this process is impact strength polystyrene, which is resistant to impact and fragility.
This plastic material, more precisely, includes properties such as strength and hardness of polystyrene and flexibility and impact absorption of polybutadiene. For this reason, these polymers are called high impact polystyrene (HIPS).
High impact polystyrene (HIPS) is a product with low fragility and higher impact strength compared to polystyrene. It is used in the manufacture of home appliances or various types of 3D printers due to its high impact resistance.
In this article, we are going to get acquainted with the method of measuring HIPS impact strength and related standards. The impact test is one of the most important mechanical tests to measure the impact resistance of polymers.
Impact test can generally be used in cases such as measuring the material resistance to impact, investigating the effect of temperature on impact strength, examining the degree of sensitivity of materials to the gap (notch), evaluating the characteristics of the cross-sectional area of failure. It is also used to estimate and classify brittle fracture behavior to correctly select materials under specified stress and temperature conditions.
Standard tests to measure impact strength
The impact test is a simple and standard test to identify and measure the tendency of a material to break. Its basis is to determine the amount of energy required to break the part due to impact.
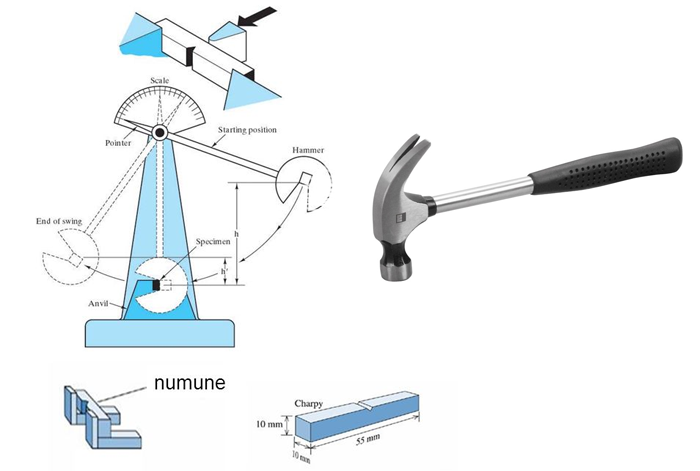
The tester consists of a pendulum that strikes the sample as it moves. The main quantity measured in the impact test is the energy absorbed in the failure of the sample. The difference in pendulum height before and after impact indicates the energy absorbed by the sample, which is usually defined as the energy on the surface.
If the amount of this energy is small, it can be concluded that the material is highly sensitive to impact forces. But if the amount of absorbed energy is high, the material is soft and malleable and can withstand more impact force, and has a higher toughness.
The amount of energy obtained is a measure of the toughness of the material and can be calculated from the difference between the initial and final angle of the pendulum.
The toughness of a material is its resistance to crack propagation or its ability to absorb energy in plastic deformation. This indicates that something can be done without breaking the unit of matter. The material with high toughness has an optimal combination of flexibility and strength.
The most common methods of impact testing are the two methods of Izod and Charpy. In the Izod method, the test sample is placed vertically and in the Charpy method, the test sample is placed horizontally. Also in the Izod test, a slit or notch fixed in a ball pendulum is hit.
While in the Charpy test, the gap is placed away from the impact ball. Another difference is that in the Charpy method, there are two types of gaps (U and V-shaped), while in the Izod method, there is only one type of gap.
Izod and Charpy tests can be applied to a wide range of plastic and composite polymeric materials. Typically, the Izod test is used to measure the strength of polystyrene against impact, which will be discussed below.
The Izod impact strength test
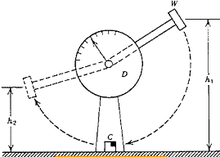
IZOD Test
As mentioned, the Izod impact strength test is used to measure the impact strength of plastics such as HIPS polystyrene. This is done according to national standard 6981 and ISO 180 and ASTM D256 standards.
The equipment required for the Izod impact test includes a pendulum impact device with suitable support and a micrometer to measure the dimensions of the test and the depth of the gap. The test sample of HIPS can also be prepared by extrusion, compression molding, or injection.
The dimensions of the HIPS sample according to ASTM D256 standard are length 64 mm, width 12.7, and thickness 3 to 12.7 mm. The type of sample slot should also be V-shaped. HIPS samples must have surfaces perpendicular to each other and without twisting.
Surfaces and edges should be free of scratches, cavities, and dents. Samples that do not meet one or more of the requirements for measurement or visual observation should be rejected. Or re-machined to the appropriate size and shape before starting the test. The Izod test usually uses 10 HIPS samples.
In this method, the polymer material is placed vertically in the clamp holding the sample. Now the pendulum goes up to the height specified in the device and is fixed in place. The hammer or pendulum is then dropped to strike the desired location in the sample.
The Izod impact strikes the sample at a certain distance from the closing point of the HIPS sample and in the slotted specimens, at a certain distance from the center of the slit to the sample. The amount of energy absorbed by the HIPS sample is recorded in the device. Sample impact strength is obtained by dividing the recorded energy by the effective surface of the sample.
The effective surface area of the sample is the product of the thickness multiplied by the width of the sample in the non-slit mode. In the case of the slit, the thickness is multiplied by the remaining width behind the slit.