Tensile strength is used to evaluate the deformation of High Impact (HIPS) polystyrene and to ensure its quality and hardness. In addition, this test is performed to determine the maximum stress that the material can withstand, as well as the tendency to flexibility and deformability.
The tensile test, which is performed to measure the tensile strength of polymers, is one of the most important and widely used tests of the mechanical properties of polymers. Its results also play an important role in the selection of materials for the production of polymer products.
In general, tensile properties are measured to develop new materials and processes, predict the behavior of a material under various forces, and ensure the quality of polymeric materials and compare them.
In this article, we will talk about the tensile strength of polymers and the tensile test used to measure the tensile strength of High Impact (HIPS) polystyrene polymer material.
Tensile strength
Tensile Strength measurement
Stress is a parameter of pressure material is obtained by dividing the force on the effective surface of the sample in the tensile test and the strain is the displacement of the sample relative to the initial state.
As a result of tension, polymeric materials first deform elastically and return to their original state when the stress is removed.
Then, by applying more stress, they deform the plastic, that is, by removing the applied stress, the dimensions of the material do not return to their original state and the deformation and the created state are irreversible. Eventually, with more stress, the material breaks.
Tensile strength is the maximum amount of stress that a polymeric material can withstand during tension and not break. In general, the tensile strength of polymers and plastics is classified into three types and includes tensile strength at the fracture point and final strength.
Tensile strength at the fracture point is the amount of stress that a polymeric material can withstand without permanent deformation and can be measured by a tensile test using a tensile device.
Tensile strength at the breaking point is the amount of material strength at the point where the polymer breaks. The maximum stress that the polymer can withstand is also called the ultimate strength.
In the tensile test, which will be described below, tensile force is applied to the sample body, which is the High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) sample. The deformation of the sample relative to the initial state and the force diagram are recorded instantaneously (or the stress diagram applied in terms of strain) in the traction device.
The linear part of this curve, which is initially elastic to the point of fracture deformation, is called the elastic region. As mentioned, in this region the relationship between stress and strain is linear. The waxy or plastic region of this curve also begins after the fracture point (the beginning of the deformation of the sample wax). The wax deformation of the sample continues steadily to the apex of the curve or tensile strength.
Many parameters can affect the tensile strength of a polymer. The most important of them are: molecular weight (increasing the molecular weight of polymers increases their tensile strength to saturation point), crosslinking (reducing strength), crystallinity (crystalline phase of the polymer due to stronger intramolecular bonds, Increases strength).
Tensile strength measurement
As explained in the previous section, with the help of the tensile test, the reaction curve of the material against the applied forces can be drawn. In this diagram, the maximum stress (final strength) is very important.
The tensile strength test of High Impact Polystyrene Copolymer (HIPS) is performed according to ASTM D638 standard.
The ASTM D638 tensile test determines the basic mechanical properties of High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) such as tensile stress, strain, tensile modulus, operating point, breaking point, and Poisson ratio. According to this standard, High Impact polystyrene (HIPS) samples with any thickness up to 14 mm can be used; Therefore, the thickness of materials with more than 14 mm must be reduced by machining to make this method feasible.
In this test, at least 5 samples of High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) must be tested.

Tensile Strength in HIPS
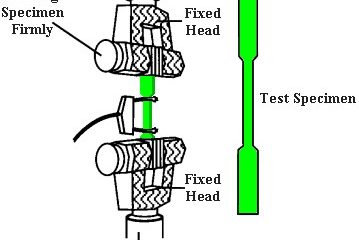
The device used in this test is a traction device that has two jaws or clamps. These jaws can generally change depending on the type of sample and its material.
The lower jaw of the device is fixed and is designed to hold the test tube firmly. The upper jaw of the device, in addition to holding the sample in itself, moves upwards and causes tensile stress to the sample.
The initial state of the sample should not be twisted before the test. Samples must be firmly seated between the jaws of the device; So that the jaws themselves do not cause the sample to rupture.
The samples are not very hard, so the jaws are not completely in the same direction, which causes a large error in the test. Therefore, it must be ensured that the jaws are aligned.
After closing the specimens and tightening them and making adjustments on the traction device software, the device is commanded to subject the specimen to the tensile stress at a certain speed (usually set at 50 mm/min). (This speed can vary according to the standard). The sample is pulled by the machine until it breaks.
The software of the device, in which the full dimensions of the sample have already been entered, can calculate and record the tensile strength at the fracture points according to the definitions mentioned in the previous sections.
If the traction device software is not able to measure the tensile strength, the force number from the device at the rupture site (for fracture points) can be divided by the effective cross-sectional area of the sample (multiplied by the thin section of the sample thickness) to obtain strength. In addition, all tensile test parameters can be viewed and measured in the stress-strain diagram.