What is the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymer? The main difference between thermoplastic and the thermosetting polymer is related to the melting of these materials. Thermoplastics can melt in any way and be reused. Regarding thermosetting polymers, we must say that these materials have a permanent shape and also cannot recycle new forms of plastic. Another major difference is the non-fragility of thermosetting polymers, which is in contrast to the fragility of thermoplastics.
In comparison, thermosetting polymers have more strength and durability than thermoplastics. In some cases, we see that thermosetting polymers are up to 10 times stronger than thermoplastics.
Investigation of structure and difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymer

Structural differences of these widely used materials
To better understand the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers, we intend to study the structure of these materials.
Thermoplastic:
Thermoplastics are a type of widely used polymer. Thermoplastic melts at very high temperatures and after the cooling process can take any shape and become solid. Thermoplastics are materials that typically have a high molecular weight.
The polymer chains in these materials are joined together by forces between molecules. If there is enough energy, it will be possible to break down the intermolecular force. One of the main features of thermoplastics is their high moldability.
Regarding the reversible thermoplastic process, which is considered as the most important difference with thermostats, it should be said that by eliminating the intermolecular energies that cause this polymer to have a solid shape, we will see the melting of this material.
After cooling, the intermolecular forces return and the thermoplastic returns to the solid-state. In this way, it is possible to make different devices with it. Thermoplastics have many physical properties between the melting point and the formation temperature of solid crystals, which help to produce different products.
Thermosetting polymer
The most important difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers is that thermostats are highly resistant to high temperatures and melting. By creating cross-links between the polymer chains in this material, it can be turned into a soft and viscous polymer or a harder and stronger material than before.
To define and identify the bonds in the structure of a thermosetting polymer, it is placed in a chemically active medium and introduced by a chemical reaction. Normally, this process is interpreted as cooking.
To start this process, the thermosetting polymer is placed at a temperature above 200 ° C and is done with the help of high-energy electron beams and ultraviolet rays and the use of additives. The crosslinks present in this material are stable chemical bonds that have a very strong 3D structure when the polymer is crosslinked.
This structure shows high resistance to heating. This process is known as the irreversible process. In this process, the raw material is transformed into a polymer network that has a stable heat capability.
During cross-linking in the thermosetting polymer, the molecular weight of the polymer increases. Thus the melting point increases. Given this, we find that when the melting point is higher than ambient temperature, the material retains its solid-state; If the temperature rises uncontrollably.
These products decompose instead of melting. Some of the most popular examples of thermosetting polymer include vulcanized rubber, polyester fiberglass, bakelite, vulcanized rubber, and melamine.
Comparison of thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers
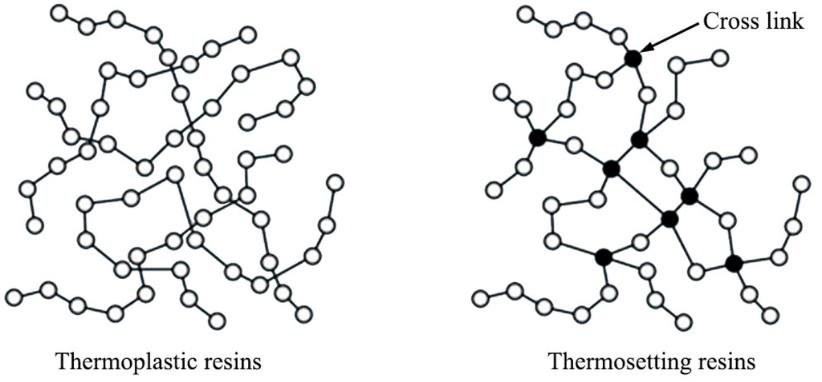
The difference between thermosetting polymer and thermoplastic
- Thermoplastics are more widely used than thermosetting polymers.
- Thermosetting polymers have higher processing costs compared to thermoplastics.
- Other features of thermoplastics in manufacturing and processing compared to thermosetting polymer have higher properties, energy, and efficiency.
- There are many materials in thermoplastics; In particular, composites that are highly prone to failure, while thermosetting polymers have a high resistance to failure.
- Thermoplastics melt very quickly, while thermosetting polymers are highly resistant to melting.
- Another case that exists in thermoplastics and is referred to as a defect of this material. That is, thermoplastics have a creeping problem while thermosetting polymers have high strength.

